A history of dyspepsia, peptic ulcer is the initial allegations. So is a history of recurrent vomiting who initially did not bleed, excessive alcohol consumption leads to the suspicion of gastritis and peptic ulcer disease. A history of recurrent vomiting who initially did not bleed more towards Mallory-Weiss. Excessive alcohol consumption leads to allegations of gastritis (30-40%), peptic ulcer disease (30-40%), or sometimes varicose veins. Weight reduction leads to the suspicion of malignancy. Heavy bleeding accompanied by a clot and refractory shock treatment increases the likelihood of varicose veins. A history of previous abdominal aortic surgery increases the likelihood of fistula aortoenterik. At the young age of patients with a history of upper gastrointestinal bleeding brief repeated (often accompanied by hemodynamic collapse) and a normal endoscopy, should be considered Dieulafoy lesion (a submucosal artery, usually near the heart, which can cause intermittent gastrointestinal bleeding that much) (Davey, 2005).
In general, patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding caused by rupture of esophageal varices have a poor liver function / disturbed so that every large and small bleeding resulting in severe liver failure. Many factors affect the prognosis of patients such as age, Hb level, blood pressure during treatment, and others.
Pathophysiology
Cari Blog Ini
Selasa, 19 April 2011
Jumat, 15 April 2011
Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease
This condition is chronic and begins when a person is an adolescent and then it slowly progresses throughout their life. Coronary artery disease pathophysiology revolves around a few theories. One widely accepted theory is that this condition occurs when the body is trying to heal itself as a result of endothelial injury. Inflammation is also beginning to be accepted as a critical component of potential plaque instability and atherosclerosis activity. Patients who have been diagnosed with established coronary artery disease and have several of the causes and/or risk factors as well are at a much higher risk of experiencing a cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction, and other vascular events in the future.
Elevated C-reactive protein levels, and other elevated biochemical markers, indicate a higher risk of experiencing a vascular event in the future and it indicates an increased likelihood of vascular inflammation. This marker may also indicate the need for aggressive preventative measures due to the patient having a quickly advancing coronary artery disease.
Source : www.brighthub.com
Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusType 1
Insulin is essential to process carbohydrates, fat, and protein. Insulin reduces blood glucose levels by allowing glucose to enter muscle cells and by stimulating the conversion of glucose to glycogen (glycogenesis) as a carbohydrate store. Insulin also inhibits the release of stored glucose from liver glycogen (glycogenolysis) and slows the breakdown of fat to triglycerides, free fatty acids, and ketones. It also stimulates fat storage. Additionally, insulin inhibits the breakdown of protein and fat for glucose production (gluconeogenesis) in both liver and kidneys.
Hyperglycemia (ie, random blood glucose concentration more than 200 mg/dL or 11 mmol/L) results when insulin deficiency leads to uninhibited gluconeogenesis and prevents the use and storage of circulating glucose. The kidneys cannot reabsorb the excess glucose load, causing glycosuria, osmotic diuresis, thirst, and dehydration. Increased fat and protein breakdown leads to ketone production and weight loss. Without insulin, a child with type 1 diabetes mellitus wastes away and eventually dies due to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
The effects of insulin deficiency are shown in the image below.
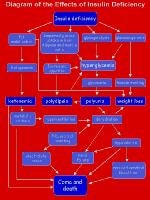
The effects of insulin deficiency.
An excess of insulin prevents the release of glucose into the circulation and results in hypoglycemia (blood glucose concentrations of < 60 mg/dL or 3.5 mmol/L). Glucose is the sole energy source for erythrocytes, kidney medulla, and the brain. Source : emedicine.medscape.com
Hyperglycemia (ie, random blood glucose concentration more than 200 mg/dL or 11 mmol/L) results when insulin deficiency leads to uninhibited gluconeogenesis and prevents the use and storage of circulating glucose. The kidneys cannot reabsorb the excess glucose load, causing glycosuria, osmotic diuresis, thirst, and dehydration. Increased fat and protein breakdown leads to ketone production and weight loss. Without insulin, a child with type 1 diabetes mellitus wastes away and eventually dies due to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
The effects of insulin deficiency are shown in the image below.

The effects of insulin deficiency.
An excess of insulin prevents the release of glucose into the circulation and results in hypoglycemia (blood glucose concentrations of < 60 mg/dL or 3.5 mmol/L). Glucose is the sole energy source for erythrocytes, kidney medulla, and the brain. Source : emedicine.medscape.com
Minggu, 10 April 2011
Pathophysiology of Typhoid Fever

Typhoid fever, also known as Typhoid, is a common worldwide illness, transmitted by the ingestion of food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected person, which contain the bacterium Salmonella enterica enterica, serovar Typhi. The bacteria then perforate through the intestinal wall and are phagocytosed by macrophages. The organism is a Gram-negative short bacillus that is motile due to its peritrichous flagella. The bacterium grows best at 37°C / 98.6°F – human body temperature.
This fever received various names, such as gastric fever, abdominal typhus, infantile remittant fever, slow fever, nervous fever, pythogenic fever, etc. The name of "typhoid" was given by Louis in 1829, as a derivative from typhus.
Pathophysiology of Typhoid Fever
Transmission of Salmonella typhi can be transmitted through various ways, which is known with 5 M of the Food Fingers, Fomitus (vomiting), Fly, and through Faeces.
Faeces and vomiting in patients with typhoid salmonella typhi can transmit the germ to others. Germs can be transmitted through the intermediary of flies, which fly will perch on the food to be eaten by healthy people. If the person is less attention to hygiene such as washing her hands and food contaminated with salmonella bacteria enter the body thypi a healthy person through the mouth. Then the germs get into the stomach, some bacteria will be destroyed by stomach acid and partly into the distal small intestine and reach the lymphoid tissue. In this lymphoid tissue breed germs, and then enter the bloodstream and reach the reticuloendothelial cells. Reticuloendothelial cells are then release germs into the bloodstream and cause bacteremia, bacteria then enter the spleen, small intestine and gallbladder.
Pathophysiology of Meningitis

Pathophysiology of Meningitis
Predisposing factors include upper airway infection, otitis media, mastoiditis, sickle cell anemia and other hemoglobinopatis, a new neurosurgical procedure, head trauma and immunological effects. Venous channels through the posterior nasopharynx, middle ear and mastoid tract to the brain and the veins near the channel meningen; all of these links that support the growth of bacteria.
Organisms enter the bloodstream and cause an inflammatory reaction in the meningen and under the cortex, which can cause thrombus and decreased cerebral blood flow. Cerebral tissue due to impaired metabolism meningen exudate, vasculitis and hypoperfusion. Purulent exudate may spread to the base of the brain and spinal cord. Inflammation also spread to the wall membrane of the cerebral ventricles. Bacterial meningitis associated with intracranial physiological changes, which consisted of increased permeability of the blood, the defense area of the brain, cerebral edema and increased intra-cranial pressure.
In acute infection patients died due to bacterial toxins, before the meningitis. The infection most of these patients with adrenal damage, circulatory collapse and associated with widespread hemorrhage (at sindromWaterhouse-Friderichssen) as a result of endothelial damage and necrosis of blood vessels caused by the meningococcus.
Pathophysiology of Meningitis
Pathophysiology of Hallucination

Pathophysiology of Hallucination
Various theories have been put forward to explain the occurrence of hallucinations. When psychodynamic (Freudian) theories were popular in psychiatry, hallucinations were seen as a projection of unconscious wishes, thoughts and wants. As biological theories have become orthodox, hallucinations are more often thought of (by psychologists at least) as being caused by functional deficits in the brain. With reference to mental illness, the function (or dysfunction) of the neurotransmitters glutamate and dopamine are thought to be particularly important. The Freudian interpretation may have an aspect of truth, as the biological hypothesis explains the physical interactions in the brain, while the Freudian deals with the origin of the flavor of the hallucination. Psychological research has argued that hallucinations may result from biases in what are known as metacognitive abilities.
These are abilities that allow us to monitor or draw inferences from our own internal psychological states (such as intentions, memories, beliefs and thoughts). The ability to discriminate between internal (self-generated) and external (stimuli) sources of information is considered to be an important metacognitive skill, but one which may break down to cause hallucinatory experiences. Projection of an internal state (or a person's own reaction to another's) may arise in the form of hallucinations, especially auditory hallucinations. A recent hypothesis that is gaining acceptance concerns the role of overactive top-down processing, or strong perceptual expectations, that can generate spontaneous perceptual output (that is, hallucination).
wikipedia
Pathophysiology of COPD
COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is a progressive inflammatory disease connecting the airways, lung parenchyma, and vasculature. It causes the damage and remodeling of the airways and lung tissue. Proper functioning of lungs is rejected continuously by COPD. Over a period of time, these changes result in more severe conditions such as pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure. The precise pathophysiology of COPD is unidentified.
The inflammatory process is a driving aspect in the pathophysiology of COPD. Recent verification suggests that the inflammatory response results in a number of effects, including an arrival of inflammatory cells such as macrophages, neutrophils and lymphocytes. Thickened airways and structural changes such as increased smooth muscle and fibrosis may also be manifested. Cigarette smoking causes an inflammatory response in the lungs. This response does not cease with the removal of the stimulus, but progresses for an unlimited period of time. COPD is a subset of obstructive lung diseases that includes cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis and asthma. Degeneration and destruction of the lung and supporting tissue are characteristic of COPD. These processes result in emphysema, chronic bronchitis, or both. Emphysema begins with a small airway disease and progresses to alveolar destruction, with a predominance of small airway narrowing and mucous gland hyperplasia.
The pathophysiology of COPD is not entirely understood. Chronic inflammation of the cells lining the bronchial tree plays a major role. Smoking and, seldom, other inhaled irritants, perpetuates an ongoing inflammatory response that results in airway narrowing and hyperactivity. Airways become edematous, excessive mucus production occurs and cilia function weakly. Patients face increasing difficulty clearing secretions with disease progression. Accordingly, they develop a chronic productive cough, wheezing and dyspnea.
The basic pathophysiologic process in COPD consists of increased resistance to airflow, loss of elastic recoil and decreased expiratory flow rate. The alveolar walls frequently break because of the increased resistance of air flows. The hyper inflated lungs flatten the curvature of the diaphragm and enlarge the rib cage. The altered configuration of the chest cavity places the respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm, at a mechanical disadvantage and impairs their force-generating capacity. Consequently, the metabolic work of breathing increases, and the sensation of dyspnea heightens.
COPD provides detailed information on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD and life expectancy, COPD medication, COPD stages and more. COPD is affiliated with Causes Of Cystic Fibrosis.
The inflammatory process is a driving aspect in the pathophysiology of COPD. Recent verification suggests that the inflammatory response results in a number of effects, including an arrival of inflammatory cells such as macrophages, neutrophils and lymphocytes. Thickened airways and structural changes such as increased smooth muscle and fibrosis may also be manifested. Cigarette smoking causes an inflammatory response in the lungs. This response does not cease with the removal of the stimulus, but progresses for an unlimited period of time. COPD is a subset of obstructive lung diseases that includes cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis and asthma. Degeneration and destruction of the lung and supporting tissue are characteristic of COPD. These processes result in emphysema, chronic bronchitis, or both. Emphysema begins with a small airway disease and progresses to alveolar destruction, with a predominance of small airway narrowing and mucous gland hyperplasia.
The pathophysiology of COPD is not entirely understood. Chronic inflammation of the cells lining the bronchial tree plays a major role. Smoking and, seldom, other inhaled irritants, perpetuates an ongoing inflammatory response that results in airway narrowing and hyperactivity. Airways become edematous, excessive mucus production occurs and cilia function weakly. Patients face increasing difficulty clearing secretions with disease progression. Accordingly, they develop a chronic productive cough, wheezing and dyspnea.
The basic pathophysiologic process in COPD consists of increased resistance to airflow, loss of elastic recoil and decreased expiratory flow rate. The alveolar walls frequently break because of the increased resistance of air flows. The hyper inflated lungs flatten the curvature of the diaphragm and enlarge the rib cage. The altered configuration of the chest cavity places the respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm, at a mechanical disadvantage and impairs their force-generating capacity. Consequently, the metabolic work of breathing increases, and the sensation of dyspnea heightens.
COPD provides detailed information on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD and life expectancy, COPD medication, COPD stages and more. COPD is affiliated with Causes Of Cystic Fibrosis.
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)
-
A history of dyspepsia, peptic ulcer is the initial allegations. So is a history of recurrent vomiting who initially did not bleed, excessiv...
-
Typhoid fever , also known as Typhoid , is a common worldwide illness, transmitted by the ingestion of food or water contaminated with the...
-
COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is a progressive inflammatory disease connecting the airways, lung parenchyma, and vasculatu...

